CMU 15-445 Lecture #14: Query Execution II
目录
CMU 15-445 Database Systems
Lecture #14: Query Execution II
Background
- 上节课讨论了DBMS的执行过程
- 这节课讨论DBMS在多线程下的执行过程
Parallel vs Distributed Databases
-
并行和分布式数据库
-
Parallel DBMSs
- 资源都在一块,离得很近
- 资源通信很高速,OS内通信
- 线程间的通信高速又可靠
-
Distributed Databases
- 资源相互之间离得很远
- 资源之间的通信很慢
- 节点之间通信的代价很高且不可靠
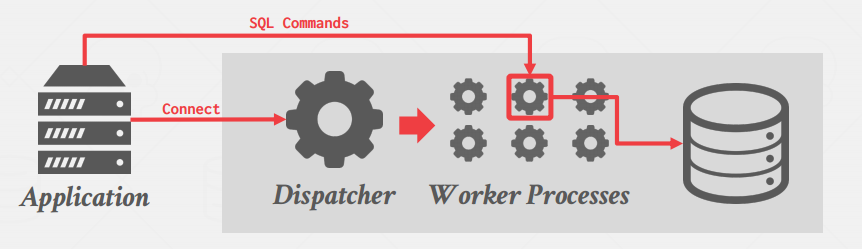
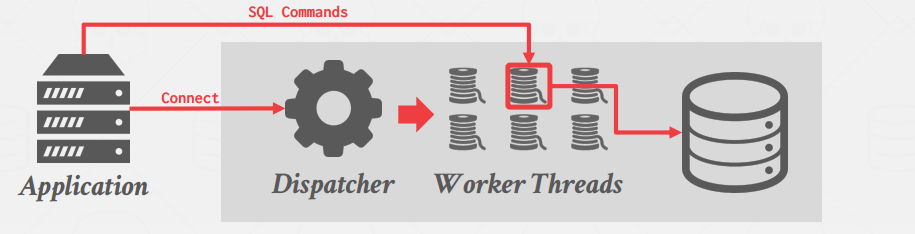
Process Models
- 模型:认为每个DBMS下面有多个worker,多个worker并行处理
- 这个模型针对的是多个SQL并发执行的问题,不能做个单个SQL并发处理的问题
- Process per Worker
- Thread per Worker
-
Scheduling
- In conclusion, for each query plan, the DBMS has to decide where, when, and how to execute. Relevant
questions include:
- How many tasks should it use?
- How many CPU cores should it use?
- What CPU cores should the tasks execute on?
- Where should a task store its output?
- When making decisions regarding query plans, the DBMS always knows more than the OS and should be prioritized as such.
- In conclusion, for each query plan, the DBMS has to decide where, when, and how to execute. Relevant
questions include:
-
说白了就是让DBMS安排一个执行计划怎么执行,这个东西和缓存一样,不能完全依赖OS线程方面的系统调用,要定制化
Inter-Query Parallelism
- 多个SQL之间怎么并发执行
- 如果并发的查询都是只读的,那冲突很小
- 如果并发的查询涉及更新数据,那冲突就很多且不可避免
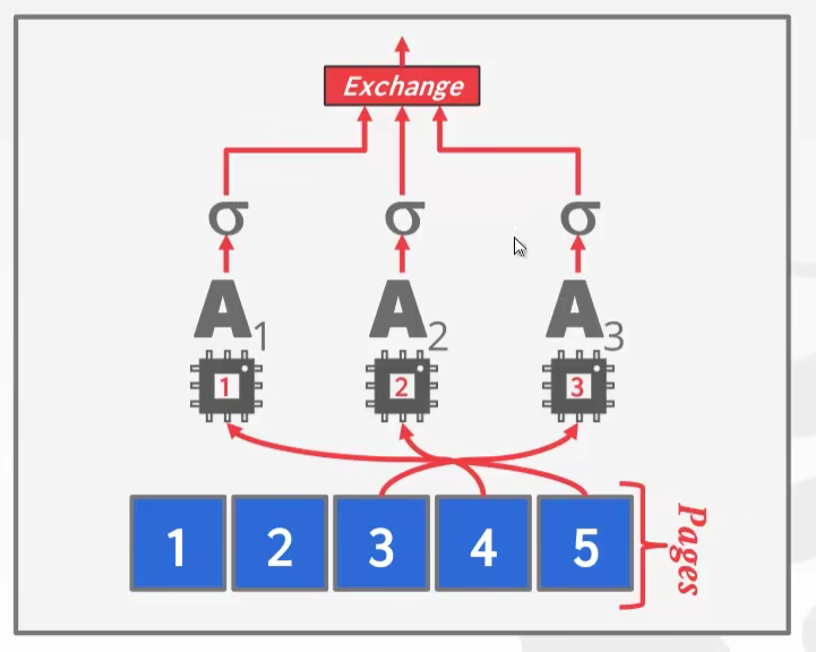
Intra-Query parallelism (Horizontal)
-
水平切,把要处理的数据给切开,然后分给多个线程,这个切是靠Exchange算子的
-
多个线程干的事情是一一样的
-

Exchange算子工作模型,并发调用 -
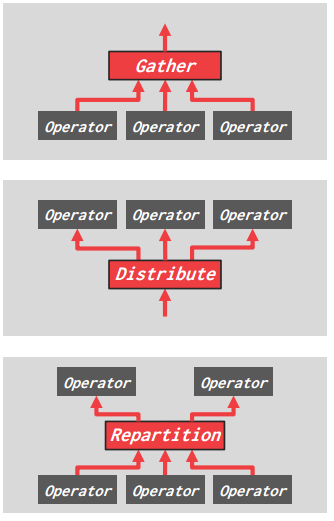
Exchange Type #1 – Gather
- → Combine the results from multiple workers into a single output stream.
-
Exchange Type #2 – Distribute
- → Split a single input stream into multiple output streams.
-
Exchange Type #3 – Repartition
- → Shuffle multiple input streams across multiple output streams.
-

三个类型的工作模型
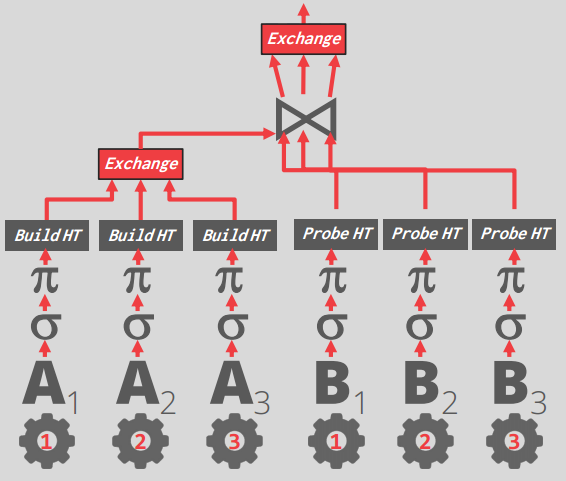
Inter-Operator parallelism (Vertical)
- 垂直切,让多个算子并发执行,数据在每个算子之间流动
- Also called pipeline parallelism.
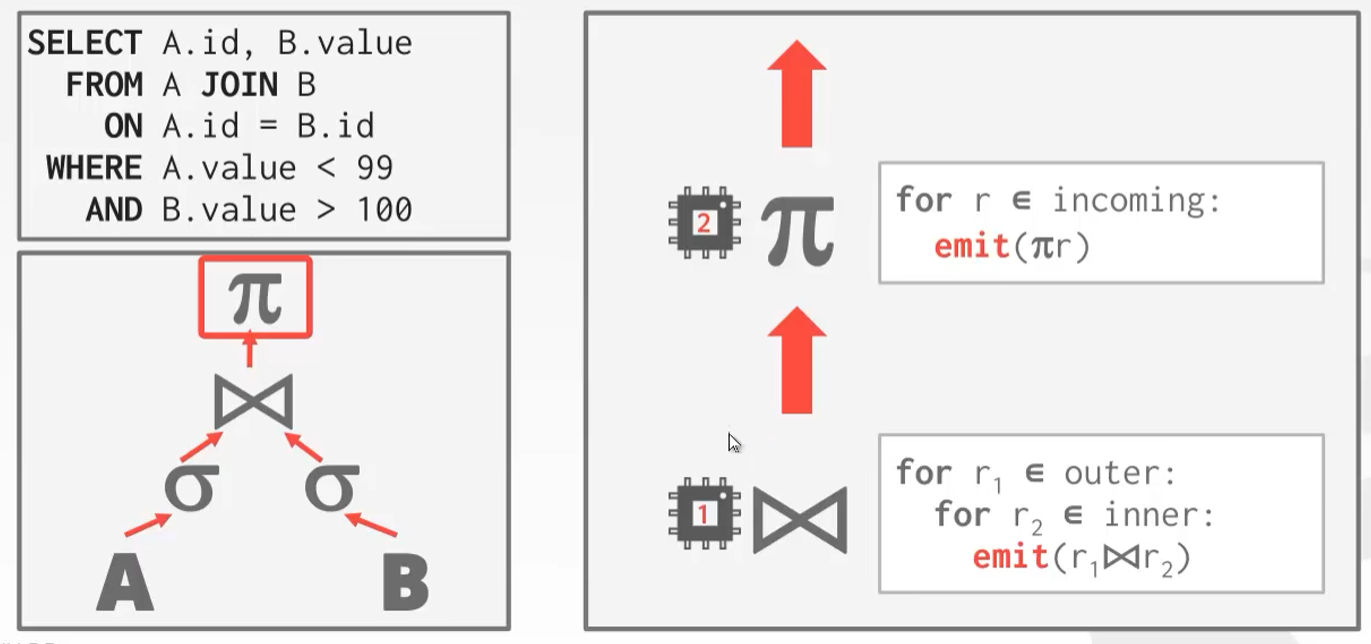
- 缺点:中间一个线程处理的速度慢,其他部分线程就要等,会浪费
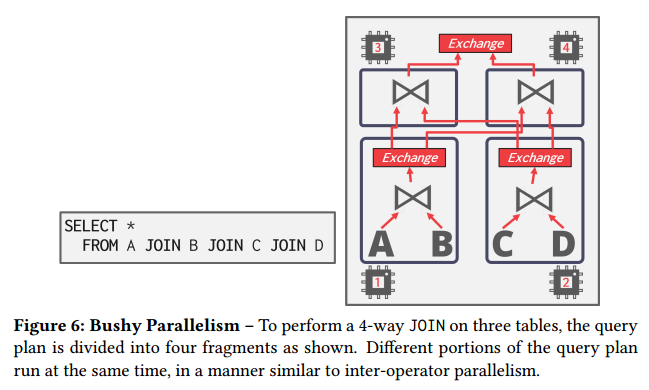
Bushy Parallelism
- 上面两种并发方式的结合
I/O Parallelism
-
上面的模型说的都是数据已经在内存中的并行,但是对于本课程的数据库,I/O带来的性能问题如何通过并行优化甚至比前面的并行优化还重要
-
还有上面的内存并行带来的问题可能是两个算子并发读写磁盘的不同部分,那对于机械盘来说这种随机读写也会大大降低性能,这部分也要进行优化
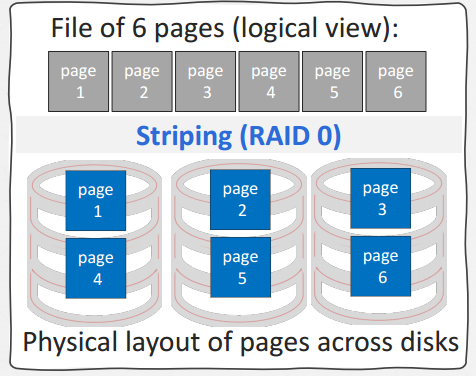
- Split the DBMS across multiple storage devices to improve disk bandwidth latency.Many different options that have trade-offs:
- → Multiple Disks per Database
- → One Database per Disk
- → One Relation per Disk
- → Split Relation across Multiple Disks
- Some DBMSs support this natively. Others require admin to configure outside of DBMS.
- Multi-Disk Parallelism
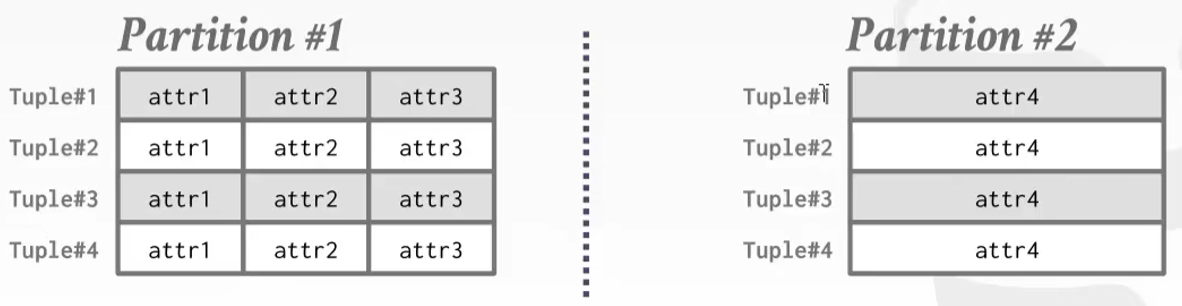
- Database Partitioning
CONCLUSION
-
Parallel execution is important, which is why (almost) every major DBMS supports it.
-
However, it is hard to get right.
- → Coordination Overhead
- → Scheduling
- → Concurrency Issues
- → Resource Contention
-
总结:并发能提示DBMS效率,但是理论简单实现难得多,要面对一大堆的问题